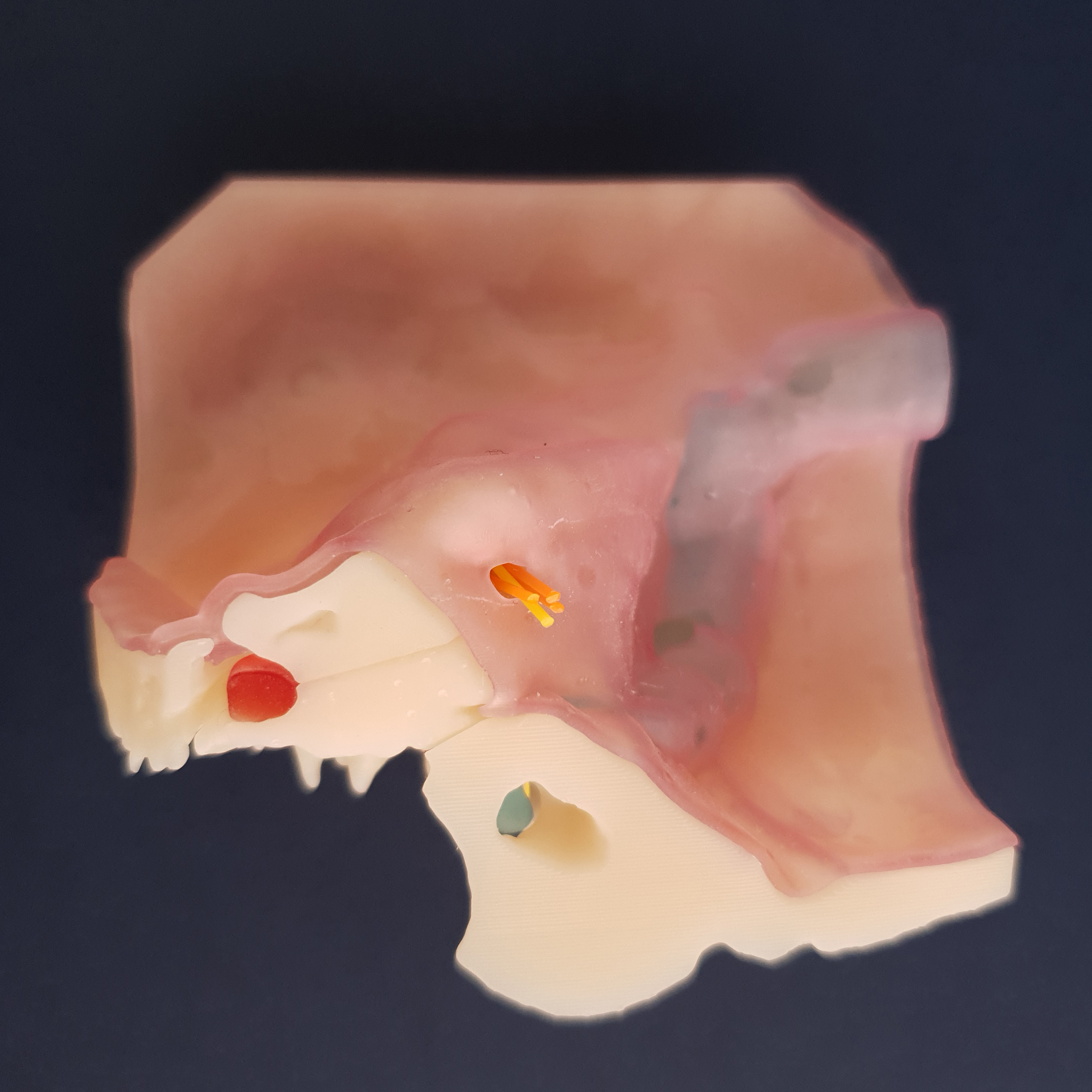
OSSO TEMPORAL ARTIFICIAL
Conheça toda a história, iniciada no Serviço de Otorrinolaringologia do Hospital das Clínicas de São Paulo
Prof Dr Ricardo Ferreira Bento
Médico Otorrinolaringologista
Professor Titular de Otorrinolaringologia da FMUSP.
“Com 35 anos de experiência em ministrar cursos de dissecção e mais de 150 cursos realizados no Brasil e em 23 países, fiquei impressionado com a similaridade dessa peça quando comparada à peça cadavérica”
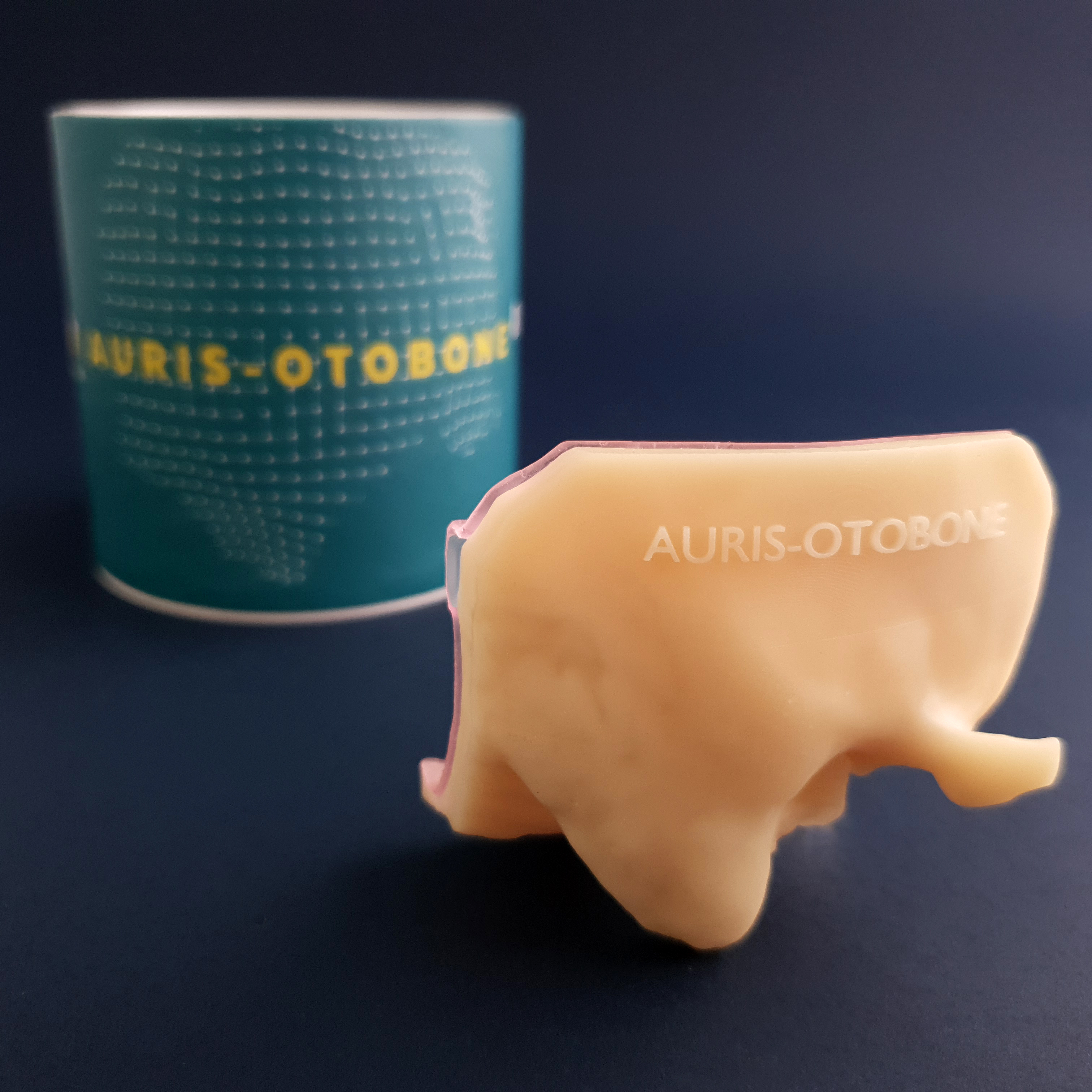
Conheça o Auris-Otobone
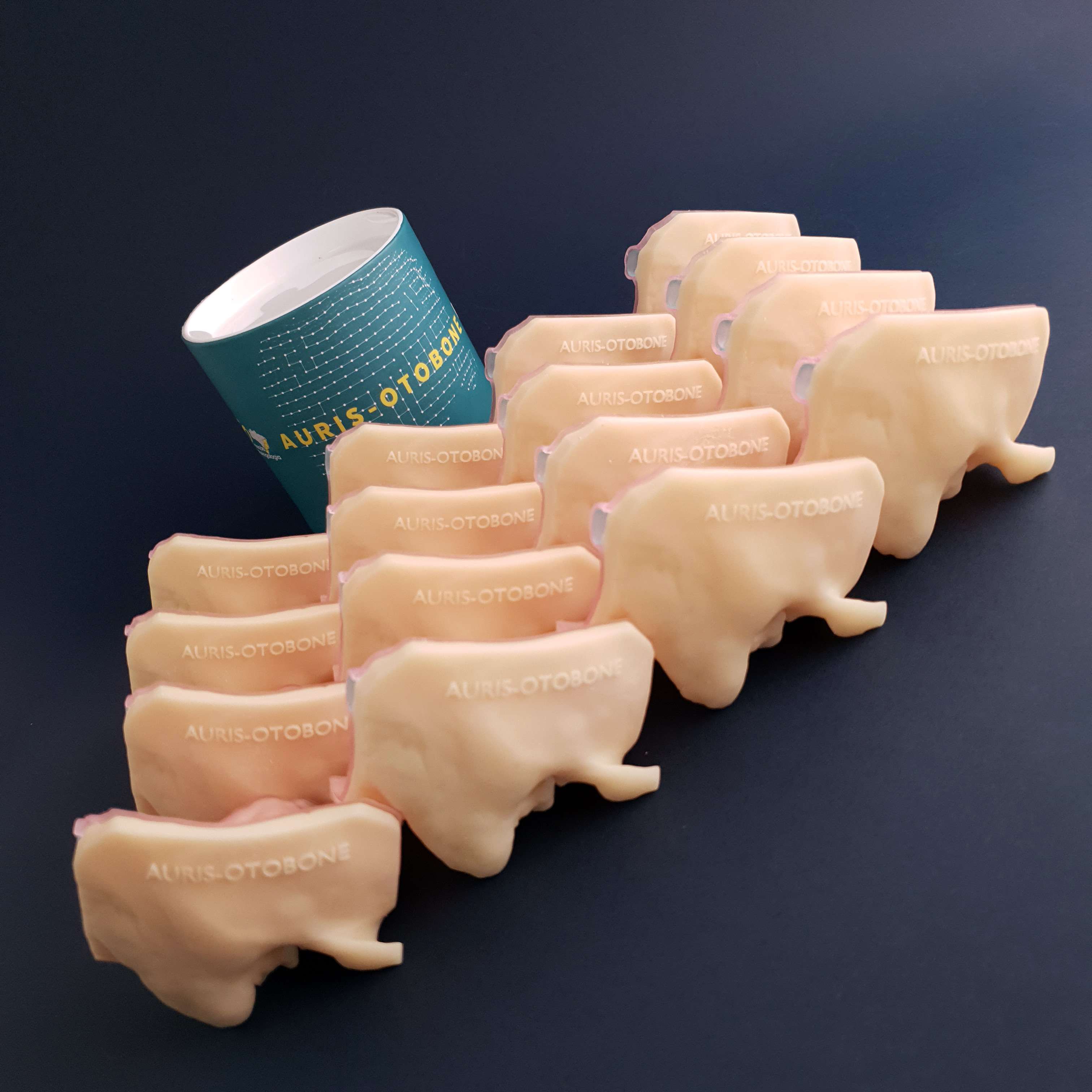
Auris-Otobone ® é um osso temporal artificial criado com o objetivo de auxiliar no treinamento de cirurgias otológicas.
Com a dificuldade de obtenção de peças anatômicas e o aumento do número de médicos Otorrinolaringologistas, houve a necessidade de criar alternativas as mais reais possíveis para treinamento cirúrgico do osso temporal.
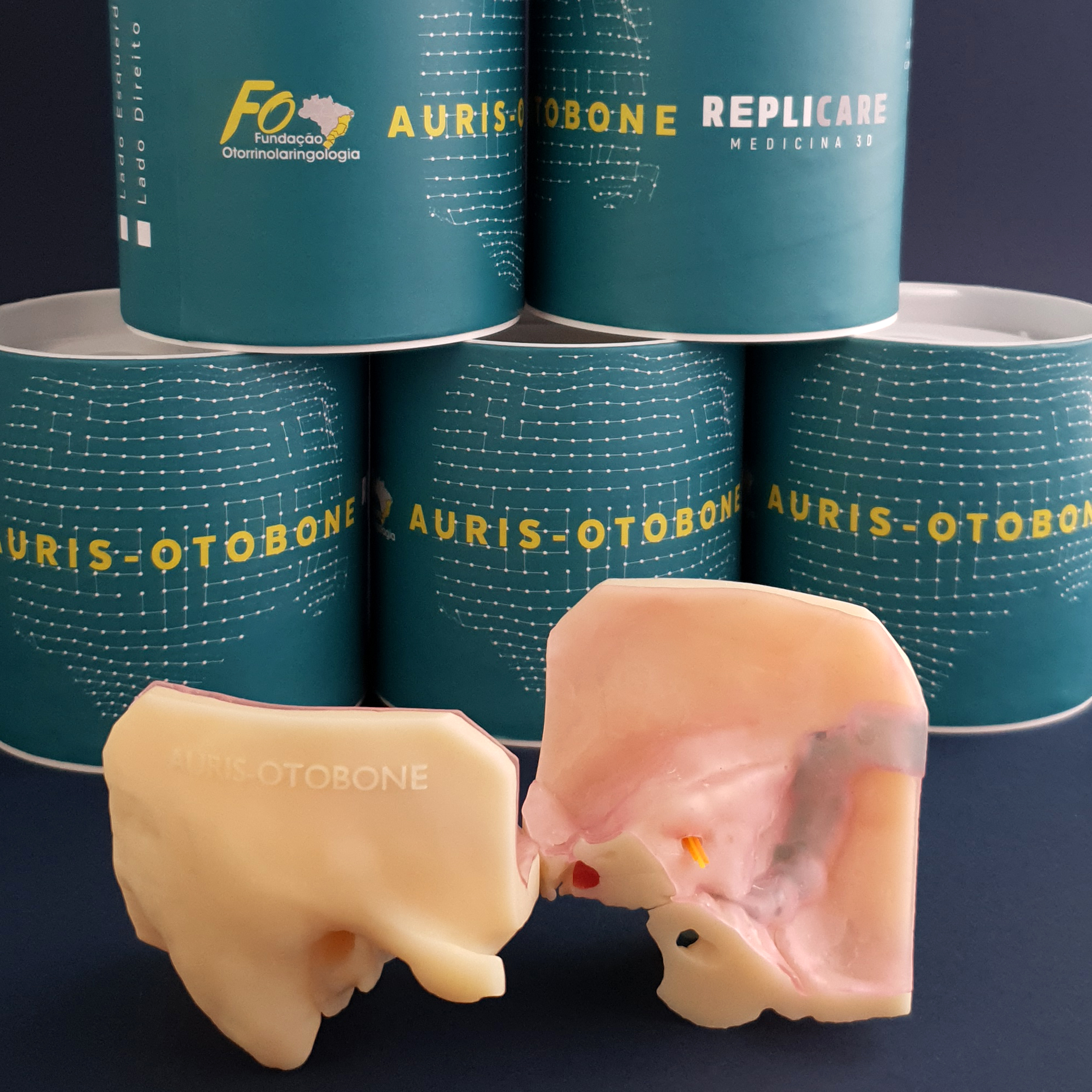
Produto desenvolvido pelo Departamento de Otorrinolaringologia da USP e Replicare – Medicina 3D, em parceria com a a Fundação Otorrinolaringologia unindo o que há de mais moderno em tecnologias tridimensionais com o exímio conhecimento médico-anatômico.
Atualmente disponível para médicos, instituições de ensino, estudantes e empresas para treinamento de próteses implantáveis em todo o Brasil e também para o exterior.
Créditos:
Prof. Dr Ricardo Ferreira Bento
Dra. Adriana Kosma Pires de Oliveira
Dra. Paula Tardim Lopes
Dr. Edson Leite Freitas
Dr. Fernando Balsalobre
Dr. Lucas Formighieri
Dr. Luiz Otávio de Mattos Coelho
Rafael Formighieri
TECNOLOGIA E BENEFÍCIOS COMPROVADOS
As características físicas e anatômicas, bem como as possibilidades de sua utilização foram objeto de estudo junto a 25 médicos (fellows, assistentes e residentes da FMUSP e de outros serviços de otorrinolaringologia), que, após a dissecção, responderam questionários anonimamente.
Seu objetivo é auxiliar no treinamento de cirurgias otólogicas
IDEAL PARA FORMAÇÃO DE RESIDENTES
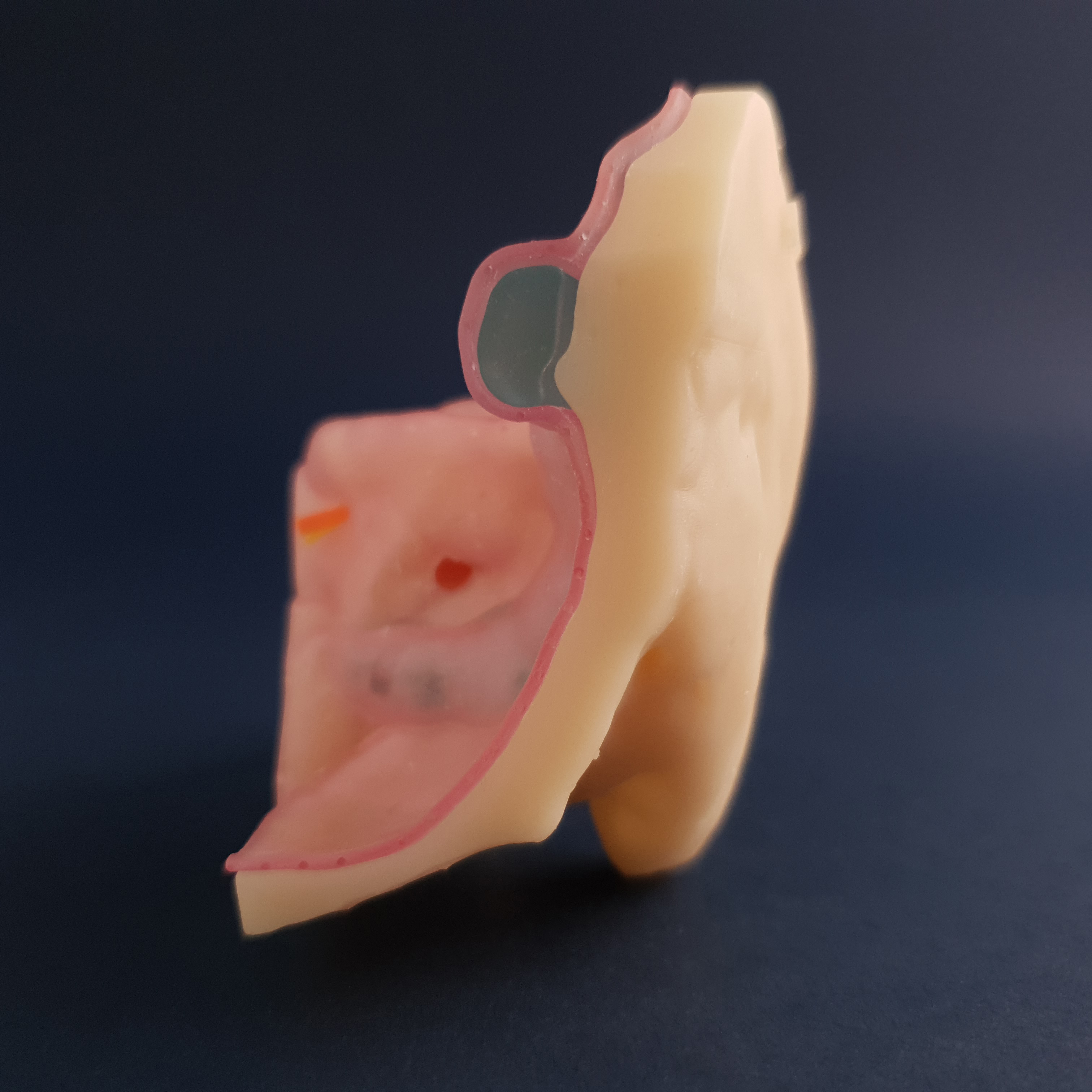
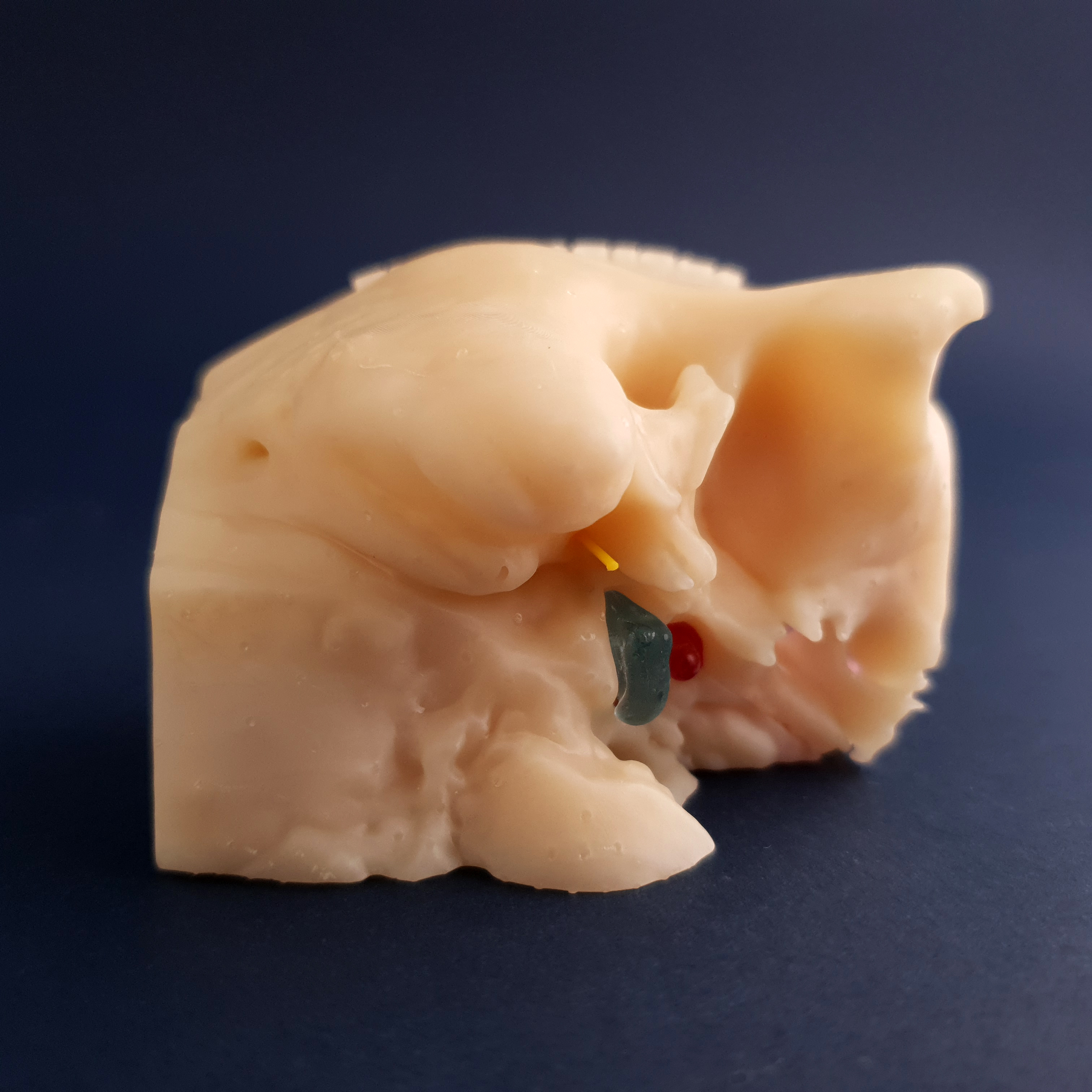
2. Reconhecimento das seguintes estruturas: Nervo Facial, Tuba Auditiva, Golfo da Veia Jugular, Ranhura do Músculo Digástrico, Antro, Ático, Cadeia Ossicular, Janelas Oval e Redonda, Seio Sigmóide e Canais Semicirculares
TREINAMENTO DE PRÓTESES IMPLANTÁVEIS
1. Implante Coclear
2. Próteses Ancoradas
IDEAL PARA RECICLAGEM DE ESPECIALISTAS
2. Timpanotomia Posterior
3. Descompressão do nervo facial
4. Labirintectomia
 Português
Português English
English